
SNC 1DI
Practice Test - Chemistry
Name: ______ANSWERS_______ Date: __________________
Multiple Choice: Circle the most correct answer.
1. Which of the following properties of sugar is not a physical property?
(a) Sugar turns black when it is heated.
(b) Sugar dissolves readily in water.
(c) Sugar has a sweet taste.
(d) Sugar is a white solid at room temperature.
2. Which of the following describes a chemical property?
(a) Hydrogen reacts explosively with oxygen.
(b) Mercury is a liquid at room temperature.
(c) Aluminum is malleable.
(d) The density of gold is 19.3 g/cm
3
.
3. All of the following are properties of magnesium. Identify the physical property.
(a) Magnesium burns in air with a brilliant white flame.
(b) Magnesium reacts with hydrochloric acid to produce a gas.
(c) Magnesium is a good conductor of electricity.
(d) Magnesium combines with nitrogen to form a black powder.
4. The use of electricity to cause chemical changes in substances is called
(a) electrostatics
(b) electrolysis
(c) electrification
(c) synthesis
5. Which one of the following is an example of a chemical change?
(a) the melting of candle wax
(b) making sawdust by sawing wood
(c) the rotting of food
(d) the breaking of glass
6. The number of electrons in the outermost orbit of a phosphorus atom is
(a) 2
(b) 8
(c) 5
(d) 15
7. Which one of the following is an example of a physical change?
(a) baking a cake
(b) cutting paper into strips
(c) bleaching a stain in clothes
(d) food digesting in your stomach
8. The least reactive element in the following list is
(a) argon.
(b) gold.
(c) potassium.
(d) copper.
9. Sulphuric acid is used in many industrial processes. If concentrated sulphuric acid has a density of 1.84 g/ml,
what is the mass of a 26.2 mL sample?
(a) 0.0702 g
(b) 14.2 g
(c) 26.2 g m=DV
(d) 28 g =(1.84g/mL)(26.2mL)
(e) 48.2 g = 48.2 g

10. Which of these ideas about atomic structure was developed by Rutherford?
(a) electrons orbit in fixed shells
(b) atomic number should be the basis for the periodic table
(c) the atom has a nucleus and an electron cloud
(d) the muffin model
(e) all atoms of an element are identical
11. To which chemical family does the element neon belong?
(a) alkali metals
(b) alkaline earth metals
(c) halogens
(d) noble gases
(e) none of the above
12. Which of the following is not a piece of evidence indicating that a chemical change has probably taken place?
(a) Bubbles of a gas appear when a solid is placed in a solution.
(b) A blue precipitate forms when two solutions are added together.
(c) A solid dissolves when added to water.
(d) An orange solid changes to grey when heated, and stays grey when cooled.
13. The granola you eat for breakfast is a heterogeneous mixture.
(a) True
(b) False
14. Which of the following is a pure substance?
(a) a soft drink
(b) milk
(c) sugar
(d) shampoo
15. Isotopes of the same element have
(a) the same number of protons and a different number of neutrons.
(b) the same number of neutrons and a different number of protons.
(c) the same number of protons and a different number of electrons.
(d) the same number of electrons and a different number of protons.
16. Which of the following is a mixture?
(a) a soft drink
(b) distilled water
(c) sugar
(d) salt
17. How much mercury (D=13.6 g/cm
3
) would it take to make 100 kg?
(a) 136 mL
(b) 7300 mL V=m/D
(c) 136 000 mL =(100000g)/(13.6g/cm
3
)
(d) 735 000 mL = 7352 mL
(e) none of the above
18. Which of the following is an example of a compound?
(a) gold
(b) orange juice
(c) hydrogen gas
(d) water
19. Air is an example of
(a) solution
(b) mechanical mixture
(c) element
(d) compound
20. One model of the atom is sometimes referred to as the "raisin bun" model. In this model, the raisins
represent the
(a) protons
(b) neutrons
(c) nucleus
(d) electrons

21. Which of the following lists of properties is characteristic of metals?
(a) Shiny, brittle, conduct heat and electricity.
(b) Shiny, malleable, conduct heat and electricity.
(c) Shiny, malleable, do not conduct heat and electricity.
(d) Shiny, malleable, conduct heat but not electricity.
22. A substance composed of two or more elements chemically combined is called
(a) a mixture.
(b) a compound.
(c) a solution.
(d) a precipitate.
23. Neutrons are
(a) negatively charged particles found outside the nucleus in an atom.
(b) neutral particles found outside the nucleus in an atom.
(c) neutral particles found in the nucleus in an atom.
(d) positively charged particles found in the nucleus in an atom.
24. The most metallic elements in the periodic table are found:
(a) on the extreme right of the table
(b) on the extreme left of the table
(c) in the middle of the table
(d) in the second column
25. Which property is described by the statement that aluminum can be bent into various shapes?
(a) density
(b) malleability
(c) hardness
(d) viscosity
26. The total number of atoms represented by the formula K
2
Cr
2
O
7
is
(a) 1
(b) 3
(c) 11
(d) 28
27. Which of the following lists consists only of metals?
(a) titanium, zinc, copper, lead, aluminum
(b) silver, chromium, oxygen, tin, copper
(c) gold, mercury, carbon, iron, lead
(d) nickel, platinum, chlorine, aluminum, silver
28. Moving down a column (family) in the periodic table, the number of electrons in the highest orbit
(a) increases gradually.
(b) decreases gradually.
(c) shows no pattern.
(d) remains constant.
29. Rows in the periodic table are also referred to as
(a) periods.
(b) families.
(c) groups.
(d) columns.
30. The element with the symbol Na is:
(a) Potassium
(b) Nitrogen
(c) Nalium
(d) sodium
31. Protons are
(a) positively charged particles found outside the nucleus in an atom.
(b) negatively charged particles found outside the nucleus in an atom.
(c) neutral particles found in the nucleus in an atom.
(d) positively charged particles found in the nucleus in an atom.

32. Electrons are
(a) positively charged particles found outside the nucleus in an atom.
(b) negatively charged particles found outside the nucleus in an atom.
(c) neutral particles found in the nucleus in an atom.
(d). negatively charged particles found in the nucleus in an atom.
33. Which group in the periodic table contains the noble gases?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 7
(d) 8
34. An element with characteristics of a metal and a non-metal is known as a
(a) noble gas
(b) alkali metal
(c) metaloid
(d) hydrogen
35. When molecules combine, they form atoms.
(a) True
(b) False
Matching: Beside each number, write the term from column B that best fits the description.
Column A Column B
_d_ 1. where electrons are located in an atom a. 8
_
c
_
_ 2. the number of electrons that the first energy shell
can hold
b. mass number
_a__ 3. the number of electrons that the second energy shell
can hold
c. 2
_
b
_
_ 4. the total number of protons and neutrons in the
nucleus
d. energy level
_g__ 5. the number of protons in the nucleus
e. ionic bonding
_
e
_
_ 6. occurs when one atom gives up its electrons to
another atom
f. covalent bond
_f__ 7. the sharing of electrons g. atomic number
Short Answer
1. Label each of the following as either a physical property or chemical property.
(a) Copper sulphate crystals are blue. ____physical_____
(b) Gold is an excellent conductor of electricity. ____physical__________
(c) Iron rusts when exposed to air and water. ____chemical___________
(d) Salt is soluble in water. ____physical___________
(e) Calcium reacts with water to produce hydrogen. ____chemical_________
(f) Gasoline burns in an automobile engine. ____chemical__________

2. State whether each of the following changes is a physical change or a chemical change.
Give a reason for your answer in each case.
(a) The snow on the sidewalk outside your house melts.
___physical – change in state from solid to liquid_________________________
(b) A piece of silverware gradually tarnishes when left exposed to air.
____chemical – new substance formed, silver oxide, change in colour_____________________
(c) Milk turns sour after several days.
___chemical – new substance forms, precipitate_________________________________________
(d) The three sugar cubes that you add to your coffee disappear when you stir the coffee.
___physical – sugar dissolves but you could get sugar back by evapourating coffee_______________
(e) You accidentally spill some bleach on your favourite blue shirt and end up with white stains on the shirt.
___chemical – change in colour__________
(f) To reconnect a loose wire in your computer, the technician melts some solder.
___physical – melting is a physical process_________________________
(g) The melting of ice cream.
___physical – melting is a physical process________________________________
(h) The mixing of cake batter in a bowl.
___physical – stirring is a physical process____________________
(e) The explosion of a firecracker.
___chemical – heat and light are produced__________________________
3. Complete the following chart.
Gas How to test for gas. What is observed if the gas is present.
oxygen
Glowing splint placed in gas
Glowing splint bursts into flames
carbon
dioxide
1. Gas poured into limewater
2. Blazing splint placed in gas
1. Limewater turns from clear to milky
2. Blazing splint is extinguished
hydrogen
Blazing splint placed in gas
Blazing splint makes a “pop” sound

4. Complete the following chart.
Gas Description Density Compared to
Air?
Does it Burn? Does it support
Combustion?
Oxygen
(O
2
)
Colourless, odourless, gas Same No Yes
Carbon dioxide
(CO
2
)
Colourless, odourless, gas
Heavier
No
No
Hydrogen
(H
2
)
Colourless, odourless, gas Lighter Yes No
Density Calculations:
Show FULL solutions for the following problems.
5. A rectangular solid measures 5.0 cm x 7.5 cm x 15.0 cm and has a mass of 6500 g.
Calculate the density of the object.
√G: l = 5.0 cm, w = 7.5 cm, h = 15.0 cm, m = 6500g
√R: V=?, D=?
√A: V = l x w x h √D=m/V
S: V = (5.0)(7.5)(15.0) D=(6500g)/(562.5cm
3
)
√V = 562.5 cm
3
√D=11.6 g/cm
3
√S: Therefore, the density of the object is 11.6 g/cm
3
6. A object whose mass is 50 g is dropped into a graduated cylinder containing 150 mL of water.
The water rises to the 350 mL mark. What is the density of the object?
√G: m = 50 g, V
start
= 150 mL, V
final
= 350 mL
√R: V
object
= ?, D=?
√A: V
object
= V
final
- V
start
√D=m/V
S: V
object
= 350 – 150 D=(50g)/(200mL)
√V
object
= 200 mL √D=0.25 g/mL
√S: Therefore, the density of the object is 0.25 g/mL
7. A piece of plastic has a density of 0.805 g/cm
3
and a volume of 550 cm
3
. What is the mass of the plastic?
√G: D = 0.805 g/cm
3
, V = 550 cm
3
√R: m = ?
√A: m = DV
S: m = (0.805 g/cm
3
)(550 cm
3
)
√m = 442.8 g
√S: Therefore, the mass of the plastic is 442.8 g
8. The density of a certain grade of gasoline is 0.750 g/mL. What volume would be occupied by 150 g of the
liquid?
√G: D = 0.750 g/mL, m = 150 g
√R: V = ?
√A: V = m/D
S: V = (150 g)/(0.750 g/mL)
√ V = 200 mL
√S: Therefore, the volume of the gasoline is 200 mL
9. Draw Bohr-Rutherford diagrams for
a. Beryllium (Be) atomic number 4, mass number 9
b. Silicon (Si) atomic number 14, mass number 28
c. Argon (Ar) atomic number 18, mass number 40
a) b) c)
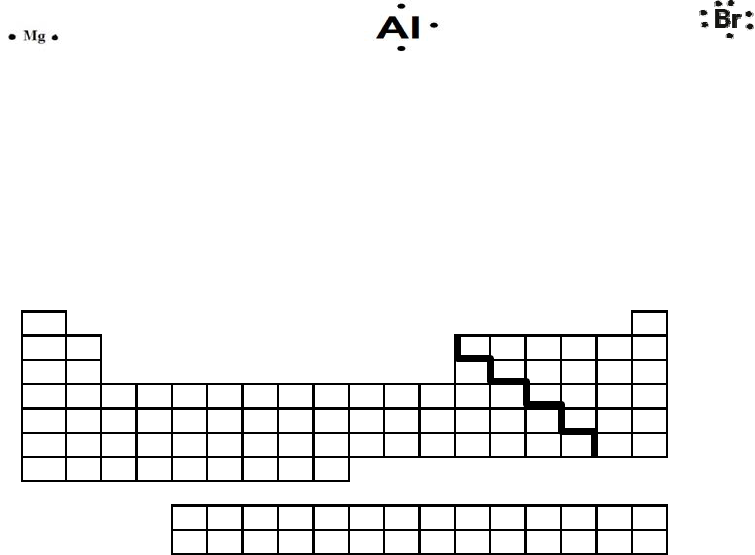
10. Draw Lewis Dot Diagrams for the following elements:
Mg Al Br
11. Indicate on the following periodic table using arrows and labels:
a. a family
b. a period
c. the division line between metals and non-metals
d. the Noble gases, the Alkali metals, the Alkaline Earth metals.
12. Fill in the blanks.
a. The __nucleus_ is the center of the atom containing most of its mass.
b. ___Nobel____ gases do not from compound with most other elements.
c. The nucleus of an atom consists of _protons_ and __neutrons____.
d. The energy levels surrounding the nucleus consist of __electrons___.
e. ___Metals_ conduct electricity, are malleable and are lustrous.
13. Describe the similarities and/or differences between each pair of terms listed below.
a. element/compound
Sim: Both elements and compounds are made of atoms
Diff: Elements contain only one type of atom. Compounds have two or more types of atoms bonded
together.
b. atomic number/mass number
Sim: Both numbers include protons.
Diff: Atomic number just includes protons. Mass number is the number of protons and neutrons.
c. family/period
Sim: Both the family and period are on the periodic table
Diff: Family is the vertical columns on the periodic table. Periods are the horizontal rows.
d. ionic bond/covalent bond
Sim: Both are ways in which elements bond to become like the Nobel gases.
Diff: Ionic bonding occurs when elements GAIN and LOSE electrons. Covalent bonding occurs when
elements SHARE electrons.
F
a
m
i
l
y
↓
Period →
N
o
b
e
l
g
a
s
A
l
k
a
l
i
m
e
t
a
l
s
Alkaline Earth metals
Halogens
14. a. Describe the apparatus used by Rutherford to investigate Thompson’s model of the atom.
Used positive, alpha particles and shot them through a piece of gold foil
b. What did Rutherford expect to see and what did he see?
Rutherford expected that all of the particles would pass straight through the foil
What he saw was that a small percentage of alpha particles were deflected and an even smaller
percentage bounced straight back
c. Describe Rutherford’s new model of the atom. What did he discover?
New model of the atom is a positive, dense nucleus with an electron cloud around the nucleus
He discovered that 1. The atom was mostly empty space and 2. The nucleus is a tightly packed, dense,
positive charge in the centre of the atom.
15. Find the element Cesium (Cs) in the periodic table. From its position in the periodic table make a prediction
for each of the following statements.
a. Is Cesium a metal or a non-metal?
Cesium is a METAL
b. Is Cesium more or less reactive than sodium?
Cesium is MORE reactive than sodium
c. Is Cesium malleable or brittle?
Cesium is MALLEABLE
d. What is its state at room temperature?
Cesium is a SOLID at room temperature
