An Overview of Complex Drug Substances and
Complex Formulations-A Quality Perspective
Katherine Tyner, PhD
Associate Director for Science (Acting)
Office of Pharmaceutical Quality
Center for Drug Evaluation and Research
U.S. Food and Drug Administration

2
Disclaimer
This talk reflects the views of the author and should not
be construed to represent FDA’s views or policies. The
mention of commercial products, their sources, or their
use in connection with material reported herein is not to
be construed as either an actual or implied endorsement
of such products by the Department of Health and
Human Services.

3
Outline
• Background to Complex Products and Quality
• Quality Considerations for Complex Drug Substances
• Quality Considerations for Complex Formulations
• Analytical and Emerging Technologies
• Helpful Tips

4
Complex Generics
As part of the FDA’s efforts to promote drug competition and patient access, we’ve
advanced many policies aimed at making it more efficient to bring generic competition to
the market. We’ve been especially focused on a category of medicines known as complex
drugs. These are drugs that, by nature of their formulation, delivery systems or the
complexity of their active ingredients, for example, are harder to “genericize” under
traditional approaches. As a result, these complex drugs often face less competition.
- Dr. Scott Gottlieb

5
Complex Products
COMPLEX of: Complex Product Type Drug Products
Active Pharmaceutical
Ingredients (APIs)
peptides, complex mixtures of APIs,
naturally sourced ingredients
Glatiramer acetate injection, Sevelamer
carbonate tablet/powder, Conjugated
Estrogens tablet
Formulations/Dosage
Forms
liposomes, colloids, transdermals,
extended-release injectables, implantables
Doxorubicin HCl Liposome injection,
Cyclosporin ophthalmic emulsion,
Etonogestrel implant, Lidocaine patch
Routes of Delivery locally acting drugs such as dermatological
products, complex ophthalmological
products
Acyclovir topical cream/ointment,
Prednisolone acetate ophthalmic suspension
Drug-Device
Combinations
dry powder inhalers, metered dose inhalers,
nasal sprays, auto-injectors
Mometasone furoate nasal spray, Fluticasone
propionate and Salmeterol inhalation powder,
Epinephrine auto-injector
Other products
complexity or uncertainty concerning the
approval pathway or possible alternative
approach would benefit from early scientific
engagement
Abuse deterrent opioid formulations
https://www.fda.gov/downloads/ForIndustry/UserFees/GenericDrugUserFees/UCM525234.pdf
Generic Drug User Fee Amendments (GDUFA) II Commitment Letter:

6
Complex Generics
Our aim is to enhance transparency, provide greater clarity and scientific guidance for
generic drug developers, and support the availability of high-quality, safe and effective
generic medicines.
- Dr. Scott Gottlieb

7
Pharmaceutical quality is
consistently meeting standards
that ensure every dose is safe
andeffective, free of
contamination and defects.

8
Quality Is a Shared Responsibility
• FDA’s Goal: Ensure industry can manufacture
products that consistently safely deliver their
intended benefit to the patient.
• Industry: Understand and manage their
manufacturing processes and expand the
product/process body of knowledge to facilitate
continual improvement (ICH Q10).
www.fda.gov

9
A Generic Drug Submitted to FDA for Approval
Must Demonstrate:
• The generic drug is “pharmaceutically equivalent” to the brand
• The manufacturer is capable of making the drug correctly
• The manufacturer is capable of making the drug consistently
• The “active ingredient” is the same as that of the brand
• The right amount of the active ingredient gets to the place in the body where it has
effect
• The "inactive" ingredients of the drug are safe
• The drug does not break down over time
• The container in which the drug will be shipped and sold is appropriate.
• The label is the same as the brand-name drug’s label
• Relevant patents or legal exclusivities are expired
https://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/ResourcesForYou/Consumers/BuyingUsingMedicineSafely/GenericDrugs/UCM510852.pdf

10
Complex Drug Products
• Present challenges for demonstrating product
equivalence
• Present challenges for demonstrating product
and process control
www.fda.gov
11
Quality Considerations for Complex
Drug Substances
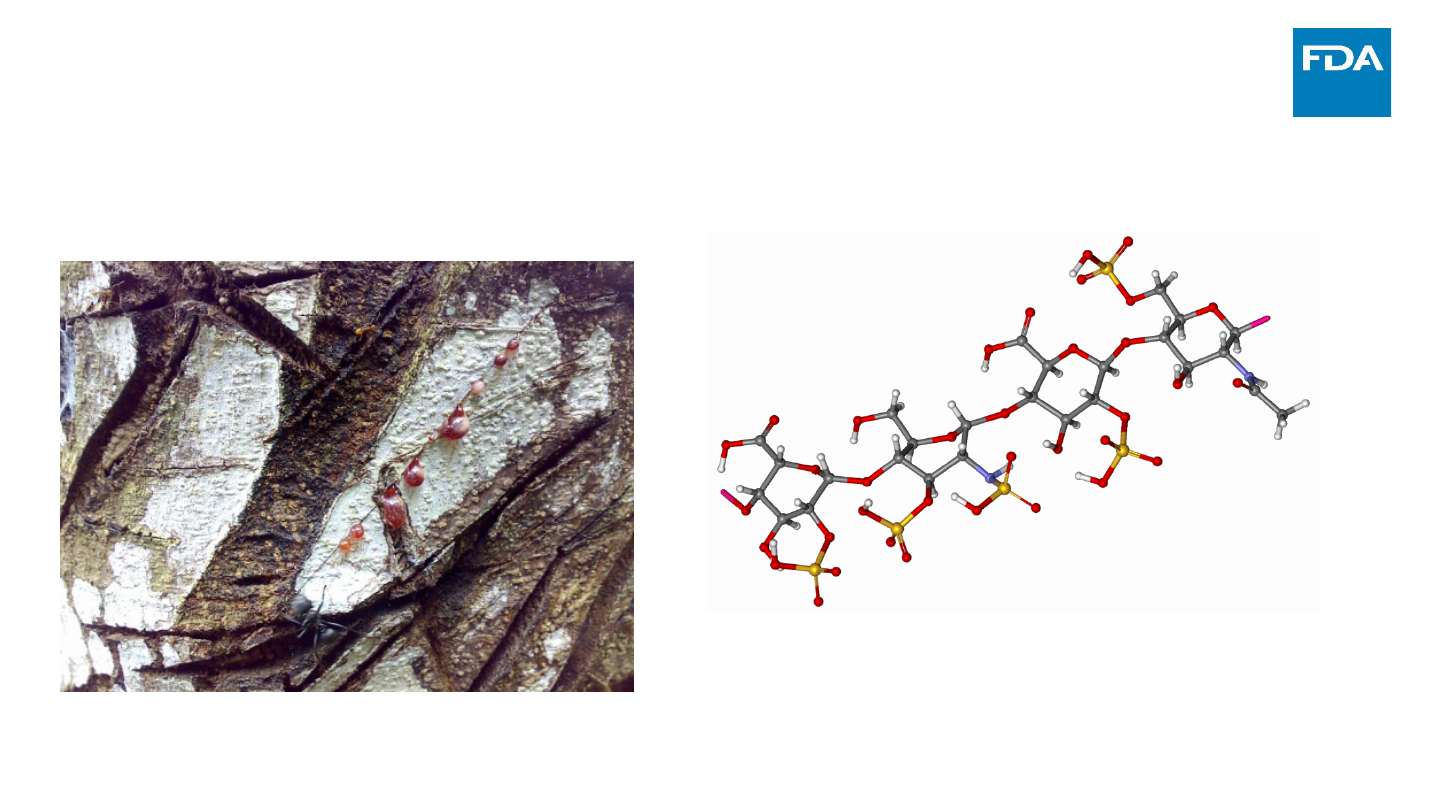
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Crofelemer#/media/File:Sangre_de_Grado.jpg
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enoxaparin_sodium#/media/File:Enoxaparin
_sodium_ball-and-stick.png

12
Complex Active Ingredients
• Sameness of the active ingredient typically determined
via four elements:
– Fundamental manufacturing scheme
– Physicochemical properties
– Structural signatures
– Confirmatory assays
• Examples
– Complex mixtures of APIs
– Naturally sourced ingredients

Slide Credit:
Andre Raw

Slide Credit:
Andre Raw

16
Quality Considerations for Complex
Formulations

17
Complex Formulations
• Sameness of the formulation structure is typically
determined via
– Physicochemical measurements
– In vitro assay (e.g. release or absorption)
• Examples
– Liposomes
– Ophthalmic emulsions

18
Case Study—Complex Formulation
• Liposome: microvesicle composed of a bilayer and/or
a concentric series of multiple bilayers separated by
aqueous compartments formed by amphipathic
molecules such as phospholipids that enclose a
central aqueous compartment
• Liposome Drug Product: a drug product in which the
active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is contained
in liposomes
• There are 12 FDA approved drug products containing
liposomes
– Commonly used to alter the biodistribution of an API
Draft Guidance for Industry. Liposome drug products, chemistry, manufacturing, and controls; human pharmacokinetics and bioavailability; and labeling documentation. U.S. Food and
Drug Administration.
http://www.fda.gov/downloads/drugs/guidancecomplianceregulatoryinformation/guidances/ucm070570.pdf (2015)
www.fda.gov

19
Liposome Drug Products are Complex Formulations
• Components of the liposome
– Lipids
– Other excipients
• Physical and chemical stability
– Chemical degradation of lipids may form
lysolipids
– Liposome fusion
• In vitro release
– Discriminate between acceptable and non-
acceptable batches of the drug product
• Complex physicochemical testing
R
1
R
2
R
3

20
Liposome Drug Products Involve Complex
Physicochemical Testing
• Suitable analytical methods need be employed to properly
characterize liposome drug products, which can often be
difficult given the complexity of liposome drug product
formulations
• Use of inappropriate methods could produce false results,
thereby calling into question data reliability and, hence,
product quality
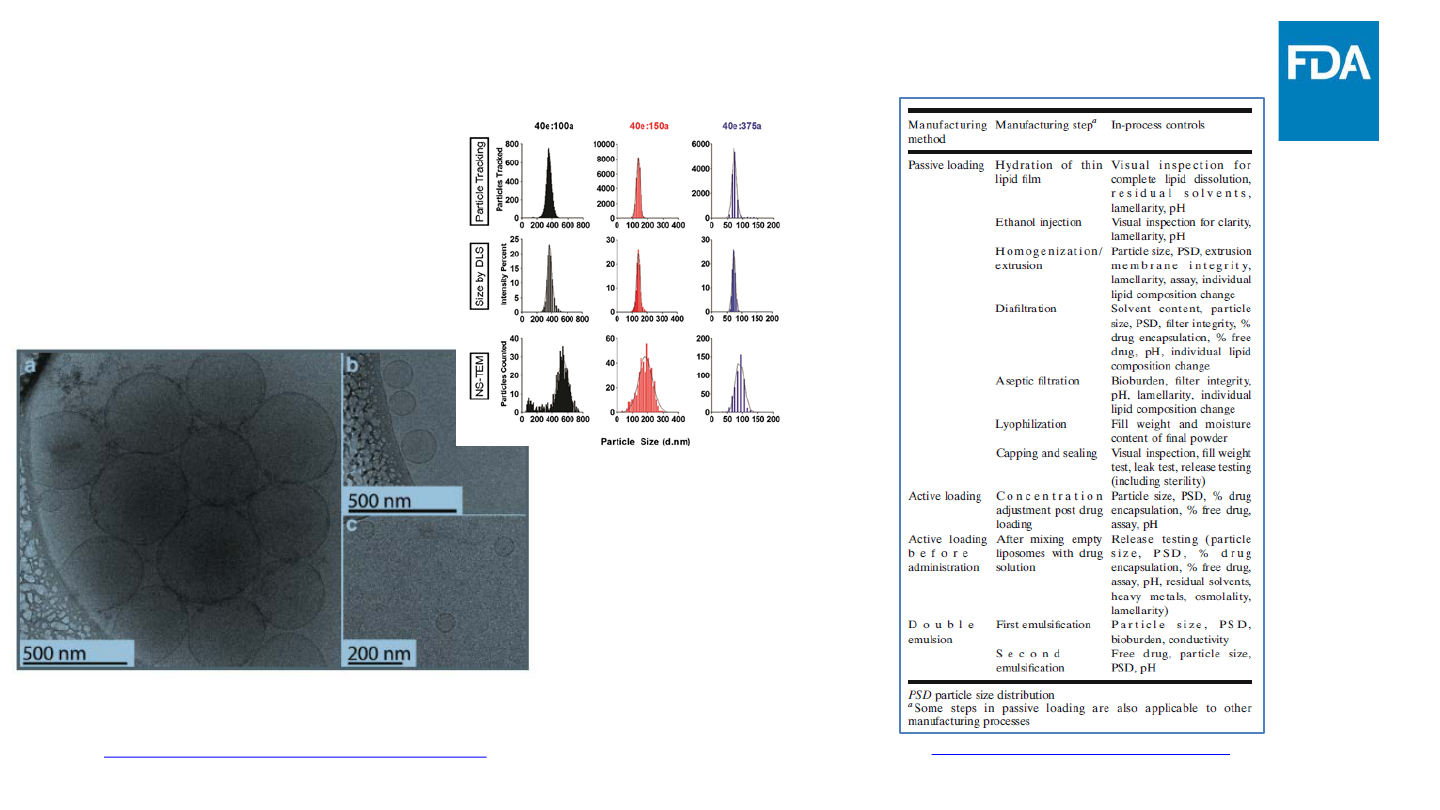
• Particle size is a critical quality attribute for liposome drug
products
– Impacts ADME, stability, drug release, etc.
– Multiple techniques, such as dynamic light scattering (DLS) and
electron microscopy (EM), are usually recommended to
thoroughly characterize particle size and size distribution
• Size is not the only attribute that needs to be characterized
– Morphology, drug loading, drug leakage etc.
www.fda.gov

21
Summary of Quality Issues for Liposome Drug Products
Kapoor M. et al. AAPS J 19(3) 2017
Challenges
(1) Identification and appropriate characterization of critical quality attributes
(2) Suitable control strategies

23
Analytical and Emerging Technology
Mass Spec
Dissolution
NMR
SEM
Gas Chromatography
High Performance
Liquid Chromatography
XRPD
Particle Sizing
Compression
Machine
Continuous
Manufacturing
3D
Printing
Slide Credit:
OTR

24
Analytical and Emerging Technology
• The properties, characterization, and methods of characterization may be different
than what is typical for other drug products
• These challenges do not reduce the adequacy and standard requirements of the
analytical methods
– Guidance for Industry: Analytical Procedures and Methods Validation for Drugs and Biologics
• Instrumentation and methodology for characterization of complex drug products is an
evolving area
– Appropriate validation and justification of the method is critical
• It is often necessary to utilize multiple complementary or orthogonal techniques
– Different methods can provide various key aspects of an attribute and thus provide a more
complete characterization picture of the drug product

25
Analytical and Emerging Technology
• Challenging vs impossible
• Difficult vs infeasible
• Rapid advancements in
analytical techniques foster
the development of complex
products
Picture Credit: Xiaoming Xu and Erin Wood

26
Helpful Tips

27
Consensus-Based Standards
• Development of technical voluntary consensus standards
– Performance characteristics of dosage forms
– Testing methodologies
– Scientific protocols
• CDER participates in committees of several standards setting
organizations
– ASTM International
– International Organization for Standardization
• CDER Standards Recognition Program
– https://www.fda.gov/ucm/groups/fdagov-public/@fdagov-drugs-
gen/documents/document/ucm631269.pdf
27
http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/GuidanceComplianceRegulatoryInformation/Guidances/UCM386366.pd

29
Emerging Technology Program
29
• Supports industry’s development and
implementation of innovative approaches in
pharmaceutical design and manufacturing
• Identifies and resolves potential scientific and
policy issues related to new approaches
– Enabled the approval of the first switch from
batch to continuous manufacturing (CM) process
for an approved drug
• A website and Guidance for Industry are
posted

30
Take-Aways
• There are many forms of complexity within drug products
• Complexity in drug products can translate to complexity in identifying,
establishing, and maintaining quality
• A suite of analytical techniques is often needed in order to adequately
demonstrate product quality
• There are multiple ways to interact with FDA during the development
of complex products
www.fda.gov