
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 07 Issue: 08 | Aug 2020 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
© 2020, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page 4384
Comparative Analysis of Python and Java for Beginners
Mrs. Selina Khoirom
1
, Moirangthem Sonia
2
, Borishphia Laikhuram
3
, Jaeson Laishram
4
,
Tekcham Davidson Singh
5
1
Assistant Professor, Dept. of Computer Science & Engineering, Manipur Institute of Technology,
Manipur-795004, India
2-5
B.E. Student, Dept. of Computer Science & Engineering, Manipur Institute of Technology, Manipur-795004, India
---------------------------------------------------------------------***----------------------------------------------------------------------
Abstract - Coding and programming are all around us
and it will keep getting more widespread in the future. One
way to make a career in the field of IT is by learning to
program. Choosing a beginner-friendly programming
language is a very important and critical choice for a
beginner in the path of becoming a programmer. If a
beginner is to choose a complex language when just starting
in this field, then one could very easily lose interest in the
field of programming. There are many programming
languages that it becomes very confusing for a beginner to
decide which language to start. This paper includes a
comparison of the two most popular, top-ranked, and in-
demand programming languages Python and Java. A brief
overview of Python and Java including its features,
applications, advantages, and disadvantages is presented in
this work. The comparison of the two languages is based on
syntax and features comparison. The paper also includes the
implementation of a simple quick sort algorithm and a
game called Tic-Tac-Toe in both the mentioned languages.
The comparison result will also be focused on the ratio of
lines of code (LOC), file capacity, and speed. We are to
conclude which programming will be much better for a
beginner.
Key Words: Comparison, Python, Java, Programming
Language, Beginner.
1. INTRODUCTION
The idea that programming is an inborn trait is a myth.
When teaching how to read, we usually take shorter books
including simple, elementary words and not a classic
novel. Similarly, we just need to apply the same in
programming also. Solving easy and simple problems
helps in building the confidence to solve complicated
problems [4]. Computational Thinking is essential
especially for a person associated with Computer Science.
The argument to determine which programming language
to be chosen by a novice has been an on-going controversy
[10]. Programming Language is the terminology used to
communicate between machines and human beings.
Computers do not understand human language so we need
a language that machine usually understands. It gives
instructions to the computer what to do next so as to
perform a task or solve a problem. The first programming
language officially proposed was Plankalkül, developed
by Konrad Zuse for his Z1 computer between 1943 and
1945 although not implemented for the time being. The
first functioning high-level programming language is
known as the Short Code proposed by John Mauchly's in
1949 and was written in the early 1950s. Fortran
(Formula Translation) was the first commercially
available language developed by a team at IBM in the year
of 1954. Programming and Coding are often used as
interchangeable words, but we need to understand that
knowing how to code does not mean you can program.
Coding is the ability to write code with the knowledge of
the syntax and structure of a language while Programming
is the capability to transcribe an idea to solve a problem
and it comprises coding, analyzing and implementing
algorithms, understanding data structures, and solving
problems.
There is a large scope for a Computer Science degree
holder and they can strive in any field. Nowadays, there
are many programming languages available and each one
of them is better than the other in their own aspects. To
choose only one programming language is tough. There
are many different factors to be considered when choosing
a language. Inaccuracy and misinformation of
characteristics of a programming language like third party
support, ease of understanding, speed or function, etc., can
have a huge impact when selecting a programming
language [5].
Novice thinks differently than an expert or professionals.
What is easy and can be solved in a few seconds by a
professional can take a long time and be difficult for a
novice. Novice needs to know the syntax, variable, loops,
how to iterate, etc., while professionals have already
acquired the knowledge. Novice usually struggles on how
to debug as they don’t usually know what should be
happening. Some adverse circumstances that were even
noticed at universities like Lappeenranta University of
Technology (LUT) where learners of programming failed
to pass the basic course and even if they do pass, they
were atrocious. Novice usually notices that nearly all
programming tools costly and decent Integrated
Development Environments (IDEs) perplexing. So, cheap
yet high aspect tools should be chosen [4]. Novice needs to
use small tasks and tools suitable for their standard not
for the level of a professional.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 07 Issue: 08 | Aug 2020 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
© 2020, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page 4385
To a novice, it is burdensome and complicated to learn all
the topics like object-oriented, dynamic memory handling,
etc., as they are not well equipped [4]. It is essential to
execute an explicit and relevant scheme while learning a
programming language since the first programming
language leaves a lasting impression regarding the
perception and ambition for learning programming [3].
Learner’s attention is divided if they are continuously
faced with the new programming environment. So, it is
necessary that they continue to master the environment
they are familiar with [4].
Similar fundamental building blocks are used by most of
the programming language, so it will be easy and effortless
to pick another new language if one has become proficient
in a particular language [1]. Even-though programmers
use different languages, they usually incline to use the
style and structure of their first language [6]. If
appropriate steps are commenced computer programming
is fun and easy. Thus, selecting a particular programming
language is a crucial step faced by a beginner so as not to
be perplexed and depreciate their confidence in
programming.
Among the various languages available, only Java and
Python are chosen for this paper. Popularity of
Programming Language (PYPL) Git-hub index and the
fourth Annual Developer Ecosystem Survey by JetBrains
was used to get some ideas regarding the current
programming trends [14, 13]. Java is one of the most in-
demand and popular languages and has been thriving for
around 25 years. Python is older than Java i.e., it has been
around for 30 years. Python has been soaring in popularity
for the past few years and able to challenge the popular
languages. This paper compares various characteristics
and features of both languages.
1.1 Objective
The aspiration of this paper is to analyze and recommend
which programming language will be better for a beginner
such that they do not lose interest in the field of
programming. This paper does not mean to affirm that the
programming languages mentioned in this paper surpasses
all the other programming language available and is the
best one for a beginner. Selecting a language that is
beginner-friendly is very important for a beginner.
Beginners usually do not have any knowledge of which
language to choose, so in this paper, we tried our best to
suggest a language for the novice. Selecting a particular
language and sticking to it is a crucial commitment
otherwise the learners will be perplexed and it will
deprecate their confidence.
This report focuses on Python and Java only. Python uses
very simple English and it is very easy to learn. It was built
with the concept of a beginner. While Java is also easy to
learn, it has strong community support. The job
opportunity for both languages is also very high. The
demand for developers with the knowledge of these
languages keeps on increasing. But the demands are not
able to be fulfilled as they required skilled developers so
the demand and supply chain is not linear.
The first part of the thesis focuses on the comparison of the
syntax of the two languages and observe which one is less
complicated and easy to comprehend. Finally, the
QuickSort algorithm and a simple Tic-Tac-Toe game are
implemented in the two mentioned languages.
2. LITERATURE REVIEW
Monica, N., O. Ogbuokiri, Benedette, O. Okwume (2015),
presented a report on “Comparison of python and java for
use in instruction in the first course in computer
programming” [1]. This thesis explains the comparison of
programming languages (Python and Java) based on code
size, execution time, memory consumption,
correctness/robustness, and commenting/reliability. The
job demands and salary for Java and Python developers
are emphasized in this paper. The algorithm for
computation of increasing grade point average (CGPA)
was enforced and implemented in both the language. The
result of this experiment shows that Python consumes less
memory than Java, Python has a smaller code size than
Java, Python implements faster than Java, and Java is more
robust than Python. So, Python is endorsed for instruction
in the first course in computer programming class for the
novice.
E Insanudin (2019) conducted research on the
comparison of source code implementation in Python and
Java [2]. The bubble sort algorithm is used in this paper to
analyze the comparison. The comparison is conducted
based on lines of code, file capacity, and access speed. The
same bubble sort algorithm is implemented in both the
language i.e., Java and Python. The author concluded that
python has a lesser number of codes and less file capacity
than Java and access speed of Python is also good.
A Bogdanchikov, M Zhaparou, and R Suliyev (2013)
presented a report on “Python to learn Programming” [3].
Python is used for this report as it has neatly organized
syntax and powerful tools to solve any task. Python is easy
and simple math. Some similar codes are implemented in
Python, Java, and C++ and are analyzed. Python is easy to
read and understand so, it is favorable for beginners.
Novice usually understands programming well when
Python is used. The report also presents a result of the
midterm marks of the same courses taught in Java and
Python. A hike of 16% is observed in the course taught in
Python.
Jussi Pekka Kasurinen (2007) presented a report on
“Python as a programming language for the introductory
programming course” [4]. This report analyzed the

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 07 Issue: 08 | Aug 2020 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
© 2020, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page 4386
introductory level education and pursue some common
problems among the course. Python is compared to C, C++,
and Java to prove the inference that Python is better for
the novice. The report also analyzed what to include in the
course structure and what to teach on the first
programming course. Louisiana State University and the
State University of West Georgia applied Python to their
basic programming course. The circumstances at fall
Lappeenranta University of Technology (LUT) 2005 is also
discussed in the report. Accumulating good course books
and reference material was strenuous.
Akesson Tobias & Rasmus Horntvedt (2019) presented a
report on “Java, Python, and JavaScript, a comparison” [5].
The report presents a brief comparison of three different
languages Python, Java, and JavaScript-based on three
different phases i.e., its syntax, why the specific language is
preferred than another in circumstances, and speed.
Python is said to be the easiest among the three languages
mentioned which require for lesser time to write. Java’s
strict syntax is also advantageous and favorable. Python is
portrayed as the slowest from the other two languages.
K. R. Srinath(2017) conducted a research paper on
“Python – The Fastest Growing Programming Language”
[9]. This paper explains why Python is a suitable language
for both learning and real-world programming. Why
Python is considered as the fastest growing language is
also deliberated in this paper. The most important
features of python language, the types of programming
supported by python and its users, and its applications are
also examined here. Python also has some cons like the
larger and complicated a program is, it is strenuous to
maintain and correct errors that arise; and as Python is
dynamically typed, the machine needs to perform extra
work making Python slow.
Stephen J. Humer & Elvis C. (2014) presented a report on
“a comparative analysis of the C++, java and python
language” [11]. The report is an analysis of the comparison
of Python, Java, and C++. The fundamental and advanced
features of the three languages are compared and
analyzed. Each language is evaluated based on standard
evaluation criteria of readability, simplicity, orthogonally,
portability, programming environment, and usage cost.
Java is said to be more convenient and favored than C and
C++ in its own aspects. Python is easier and requires only
a few lines of code compared to the others. Python is also
preferred due to its vast available choices for
implementation.
Kirby McMaster and his team in the year 2017 presented a
report on the comparison of Java and Python for the
coverage of Introductory Programming Concepts [12]. In
this paper, they analyzed the two languages i.e., Java and
Python by analyzing the words on textbooks that depict
essential programming perception. TextSTAT program is
adopted in this report to estimate the count of the concept
of essential programming topics listed in the sample of
Java and Python textbooks. There is an impressive
resemblance to concepts in both languages. Python array
is interchangeable with a list. The rank of correlation of
Java and Python is 0.726 and it keeps on rising. Module
and function are more preferred in Python than Java.
Similarly, thread, constructor, the declaration is more
preferred in Java than Python.
3. OVERVIEW
There are various languages that may be better for a
programmer but in this report, the team selected only two
languages as per their convenience. The selected
programming languages i.e., Java and Python are well-
established and top-ranked in renowned websites. They
are popular and the demand in the job market is quite
satisfactory. Some of the most important features of a
programming language for a beginner should be that it is
simple, accessible, credible, and easy to understand. The
team conducted some research concerning the two
languages from different sources such as research papers,
books, articles, etc. A brief study of both languages is
conferred below.
3.1 Overview of Java
The programming language, Java was proposed by James
Gosling and his team from Sun Microsystems in the year
1991 and was released in 1995 [5]. Java’s most prominent
feature is that it is platform-independent i.e., it has the
properties of WORA (Write Once, Run Anywhere). When
Java was first proposed, it was called OAK. OAK was
introduced with the perception of a programming
language that acts as a platform for connection for
appliances like VCR, TV, etc., [8]. Oracle Corporation
procured Sun Microsystems in 2009-10 and became the
proprietor of Java. Java is a compiled language that is
statically typed i.e., their variables are to be declared
before assigning values. The programs written in Java runs
faster than Python but is slower when compared with C++.
Airbnb, Uber, LinkedIn, Pinterest, Groupon, Spotify,
Eclipse, Hadoop, etc., are mostly based on Java. Big
Companies like Infosys, TCS, Wipro, HCL Tech, Naukri,
Jabong, Myntra, Flipkart, Trivago, ibibo, etc., are still using
Java.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 07 Issue: 08 | Aug 2020 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
© 2020, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page 4387
3.1.1 Features of Java
Fig -1: Features of Java
Figure 1 shown above is a diagram containing some
features of Java.
Object-oriented
Java is fully object-oriented. The OOP (Object-Oriented
Programming) helps in dealing with real-world
applications. The inclusion of inheritance,
polymorphism, abstraction, and encapsulation makes
a program an OOP.
Platform Independent
When compiling a program, it is compiled into a
platform-independent byte code which is then
executed using a Java Virtual Machine (JVM). The use
of JVM makes Java programming platform-
independent since if JVM is installed the same
program can be executed in multiple platforms [5].
Secured
Java uses its own runtime environment i.e., JVM, Java
applications are secure. Safety aspects like Type-
checking at compile time and runtime checking are
found inbuilt in Java. Java is also known for the
security that it provides. Java also lacks pointers,
which encourages security.
Robust
Java has strong memory management and it
automatically gets rid of objects that are not used. Java
consists of exception handling and types of checking
techniques. All these features of Java make it robust.
Portable
Java byte code can be transferred to any platform
without any implementation making it portable.
Multi-thread
The features of multi-threading are inbuilt in Java. It
aids in building highly interactive and responsive
applications that deal with many tasks at once. Multi
Threads share a common memory area, increase the
capabilities and performance.
Distributed
This aspect of Java allows accessing files by calling the
methods from any machine on the internet. It
supports the sharing of data and programs among
multiple computers for networking that is intrinsically
integrated into it. Java supports RMI (Remote Method
Invocation), Socket Programming, and the COBRA that
aid in sharing objects in a distributed environment.
3.1.2 Applications of Java
There are many fields that use Java in the real world. The
team conducted some research regarding the applications
of Java. A brief description of some of the common uses of
Java is presented below.
Android Applications
Java is regarded as the official programming language
for android mobile app development. Although mobile
applications can be created using Dart, Java is mostly
preferred. The Java byte code compiled runs on a
specialized virtual machine for android called Dalvik
Virtual Machine (DVM). Application creating software
like Android Studio and Kotlin is compatible with Java.
Java OOP principle gives better security, simple and
more effective with developing android applications
Desktop GUI Applications
Java can be used for the developed desktop
application. The packages such as Abstract
Windowing Toolkit (AWT), JavaFX, and Swing are
used to build GUI applications.
Web-based Applications
Java is used to create web applications with the help
of servlets, struts, JSP (Java Server Pages), etc. Java
caters easy coding and high security which facilitates
the development of applications for health, social
security, education, and insurance. Open-source e-
commerce platforms like Broadleaf provide aid to Java
in developing e-commerce web applications.
Cloud-based Applications
Cloud computing gives a low-cost result for IT
infrastructure. It presents with on-demand delivery of
IT resources through the internet comprising of
storage, servers, database, networking, and software
with the pay-as-you-go pricing model. Java has
characters that aid in development like SaaS
(Software-as-a-Service), IaaS (Infrastructure-as-a-
Service), and PaaS (Platform-as-a-Service).
Big Data Technologies
For the study of Big Data, Java is used as it is fast,
reliable, and robust. The features of Java such as
Automatic Garbage Collection and strong memory
management make it favorable for use in Big Data.
Frameworks like Apache Mahout, Apache Spark, Java
JFreechart are used by Java for engaging in Big Data.
Java is deep-seated with Open source communities
making it more favorable for all these technologies.
Big Data Technologies like Apache Hadoop, Apache
Spark, Apache Mahout, etc., are sub-projects of Java.
Features
of Java
Object
Oriented
Platform In-
dependent
Secured
Robust
Portable
Multithread
Distributed

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 07 Issue: 08 | Aug 2020 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
© 2020, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page 4388
3.1.3 Advantages of Java
Java is forthright, strongly-typed, and has strict
expectations that govern the learners to
contemplate in the correct way.
Java is easy to use, write, compile, debug, and
learn compared to other languages like C, C++, C#.
Being Platform-independent, distributed
language, supporting multi-threading, providing
Automatic Garbage Collection, etc., are some of
the boons of Java.
The use of OOP in Java enables to set up standard
programs and re-useable code.
Java has an inbuilt rich API for tasks like database
connection, networking, I/O, XML parsing, etc.
Java was developed with consideration of a
secured platform. It has a Security Manager for
each and every application where the access rules
for classes are established.
Java has a vast number of well-tested libraries and
frameworks.
Java is relatively inexpensive to maintain as it
does not count on an explicit hardware
framework.
Another interesting aspect of Java is that it has
strong community support. So, there will always
be someone who is able to help when the learner
gets stuck.
Although, Java is similar to C and C++, Java does
not include characteristics such as pointers and
multiple-inheritance.
3.1.4 Disadvantages of Java
Starting from 2019, Oracle announced that Java
Standard Edition 8 will be charged for business,
commercial, and production.
Java particularly focuses on storage and not on
the backup of data.
Memory management is costly as large memory
space is required.
Java is slower and memory consuming when
compared with C or C++.
Selecting a tool to develop a GUI is tough as Java
absolutely lags when in desktop programs.
Java codes are verbose. It fixates on being more
manageable but jeopardized with immensely
perplexing codes and lengthy information.
3.2 Overview of Python
Python was formulated in the late 1980s and enforced in
December 1989 by Guido van Rossum at Central
Wiskunde & Informatica (CWI) in the Netherlands [5, 7,16.
Python was proposed to be the heir for the ABC language
that is proficient for exception handling and interfacing
with the operating system Amoeba [7, 17]. Python was
named corresponding to Guido’s passion for the television
show Monty Python’s Flying Circus [2, 17]. Python is
interpreted and dynamically-typed programming language
which means that programmer does not need to define the
data-type of the variables and no need for compilation and
with the use of the interactive command-line, they get
prompt assessment without having to wait for the whole
program to be finished. Python Software Foundation (PSF)
is a non-profitable organization entrenched as the
intellectual owner of Python since version 2.1 [2]. Python
has become the fastest-growing language. The popularity
of Python in data science is one of the main reasons for the
hike of Python [9]. Some software programs that are
written in Python are YouTube, Google, Instagram, Reddit,
Spotify, Dropbox, Quora, etc. Companies like IBM, Disney,
NASA, Instagram, Spotify, Amazon, SurveyMonkey,
Facebook, etc., use Python.
3.2.1 Features of Python
Fig -2: Features of Python
Figure 2 shown above are some common features of
Python.
Easy
Python is easy to code and easy to read as
compared to other languages like Java, C, C++, etc.
Python syntax can be studied by anyone during a
short period of time. Python code is like English
that allows the learner to focus on the result.
Expressive
Python can execute a complicated function with
only a few lines of code compared to other
languages.
Free and Open Source
Python is open source and freely available. The
public can assist and contribute to the
improvement of the language. The Python source
Feature
s of
Python
Easy
Expressive
Free and
Open
Source
High level
language
Portable
Interpreted
language
Object
Oriented
Extensible
&
Embedded
Large
standard
library
Dynamically
typed

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 07 Issue: 08 | Aug 2020 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
© 2020, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page 4389
code can be downloaded, changed, used, and be
distributed.
High-level language
Python is a high-level language. There is no need
for remembering the architecture and memory
management which makes python very favorable.
Portable
Python is said to be portable as the same program
written in Python can be executed in different
platforms such as Windows, Linux, Unix, etc., if
system-dependent features are avoided.
Interpreted Language
Python is an interpreted language. The code does
not need compilation, they are executed line by
line and not all at a time which makes debugging
the code easier than all the other languages. So,
Python is slower than Java due to this feature.
Object-Oriented
Python supports an object-oriented approach
which helps the programmer to write reusable
code and aid in developing the application with
lesser code.
Extensible and embedded
The extensible property of Python allows code to
be written and compiled in other languages like C
or C++. This code then can be used further in
Python when required. The embedded property of
Python allows is allowing the use of Python in
another programming language.
Large Standard Library
Python along with the large standard library
provides for a large range of modules and
functions. So that the programmer does not need
to write the code, they can just import it
Dynamically Typed
Python is said to be a dynamically typed language
because it does not need to specify the data-type
of the variable while declaring it. The type of
value is decided during the run time.
3.2.2 Applications of Python
There are many uses of Python but the team only selected
some common applications. The applications of Python
are shown in brief below.
Web development
Python is a go-to language for web development.
Django, Pyramid, Flask, Bottle are some of the
frameworks offered by Python. Python web
frameworks are popular for their security, scalability,
and flexibility. Requests, Beautiful Soup, Paramiko,
Feedparser, Twisted Python, etc., are libraries that
also included in the Python’s Package Index.
Game development
Python has many in-built libraries that are favorable
for developing a game. PyGame, PyKyra are
frameworks for game development and PySoy is a 3D
cloud game engine for Python3.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning is one of
the rising topics and will be continued in the future.
Python is popular and favorable to be used in Artificial
intelligence and machine learning due to its character
of being stable, secure, flexible, and of its various tools.
Some of Python libraries and frameworks used in
Artificial Intelligence are SciPy, Pandas, Seaborn,
Keras, TensorFlow, Scikit-learn, NLTK, Pytorch,
Accord.NET, etc.
Desktop GUI applications
Python is also used for desktop applications. GUI
toolkits and frameworks such as PyQt, PyGtk, Kivy,
Tkinter, WxPython, PyGUI, and PySide help in making
the development of eminently functional desktop
application an easy task.
Web scraping applications
A Python is a marvelous tool that can be used to
excerpt large data from a website which is then used
for job listings, price comparison, etc. Beautiful Soup,
Mechanical Soup, LXML, etc., are some tools used for
web scraping.
Data Science and Data Visualization
Python is preferred by many for the analysis and
visualization of large data. Python is associated with
statistical means to analyze and depict complicated
data by data scientists. Packages such as NumPy,
Pandas, Sci-Kit, etc., are used.
3.2.3 Advantages of Python
Python is easy to read, learn, and write. So, it is
beginner-friendly.
Lesser code is required by Python compared to
other languages for the same task.
Python is free and open-source. Thus, it is broadly
used for varied functions.
Python has large community support.
Python is dynamically typed, embedded language.
Due to its vast libraries the programmer can
execute complex functions easily.
Python is an eminently flexible programming
language.
Python is enormous for data visualization making
the reports and visual presentation of data easy to
understand.
Python provides a low learning curve due to it
being simple and easy and is a productive
language.
Python being an interpreted language executes
the code line by line. So, even if there are multiple
errors only one error will be shown at a time
without further execution when an error occurs.
Python offers multiple programming paradigms
like object-oriented programming, imperative and
functional programming, structured
programming, procedural programming [9].

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 07 Issue: 08 | Aug 2020 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
© 2020, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page 4390
Unlike Java, Python supports multiple
inheritances.
4.2.4 Disadvantages of Python
As Python is an interpreted language, it is slower
in execution when compared with other
languages.
Python is not favorable for mobile development.
Python is not preferred for memory
comprehensive task.
As Python is dynamically typed raises run time
error leading to restriction in design.
Python is used somewhat less in large companies
and businesses due to its limitation in database
access layers unlike JDBC (Java DataBase
Connectivity) and ODBC (Open DataBase
Connectivity).
The Global Interpreter Lock (GIL) of Python
allows the execution of only one thread at a time.
Python’s simplicity becomes a disadvantage when
the programmer wants to shift to other languages
like Java which have strict structure.
4. Method
The report for a comparison of the two languages Java and
Python is portrayed in this thesis. The comparison is
processed through two different paths. Java 8 is used in
EditPlus and Eclipse IDE to write all the Java code and
Python 3.7.6 is used to write Python code in Jupyter
Notebook. The first part of this thesis generally fixates on
the syntax comparison of Python and Java. Here, the team
resolved to select some basic common syntax and features
for learning a programming language. The elements
included in consideration of the report are shown in
figure 3. The second part of the thesis is an
implementation of QuickSort and a game called Tic-Tac-
Toe. They are implemented in both Java and Python and
the comparison was done using the Lines of code (LOC),
file capacity, and speed.
Fig -3: List of the considered elements.
5. Result and Discussion
5.1 Syntax comparison between Java and Python
The team conducted an analysis of all the topics
mentioned in above figure3. The findings and differences
are written below after the comparison was conducted.
Due to the limitations of time the team was not able to do
the study in many details. There were many important
features that were not able to be mentioned in this report
due to the restraint amount of time. Appendix A contains
all the figured mentioned in this section.
Variables
Variables in Python (shown in figure A1) need not be
declared with a particular datatype before assigning
the value. This makes Python dynamically typed. The
values once set can be changed to another different
type, i.e., if a variable x = 5 where 5 is an integer, in the
next step it can be changed to x= 1j where 1j is a
complex number. Multiple variables can be declared
and stored with the same value in one line using “=” or
with different values respectively separated by a ‘,’.
Python has 2 types of variables: class variable (static
Programming Language
Variable
Casting
Print Function
Comments
Separators
Indentation or Curly brackets
Operators
Strings
User Input
Conditional statements
Loops
Classes and Object
Function and Methods
Scope
Object oriented programming
Access modifier
Method Overloading & Overriding
Exception handling
File handling

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 07 Issue: 08 | Aug 2020 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
© 2020, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page 4391
variable) and instance variable which will be
discussed later.
Variables in Java (shown in figure A2) however need
to be declared beforehand along with its type.
Although a variable can be declared before without
assigning the value, it must nonetheless affirm its
datatype while declaring the variable. A variable’s
value can be overwritten but it must be of the same
datatype. Java has a keyword called “final” which
helps in preventing the value from being replaced.
Many variables of the same type can be declared using
a comma-separated list. Java has 3 types of variables:
local variable, static variable (class variable), and
instance variable.
Casting
Casting is the process to specify a data type to a
variable. In Python, the “type ()” function is used to
display the type of the value stored in the variable.
Casting can be done during the time of declaring the
variable like x=int (1.8) i.e., x=1 where the type(x) will
give an int. Another method of casting can be done
after the value has been assigned such as b=str(a),
where a=1, which means convert the integer 1 stored
in a to a string. Python type casting is shown in figure
A3.
Java has two types of casting: -
a) implicit or widening or automatic type casting:
It is the process of converting smaller data type to a
larger data type like byte to short or int to double. If
the conversion is from short to int where variable a is
a short then int b=a;
b) explicit or narrowing or manual typecasting:
It is the process of converting larger data type to a
smaller data type like double to short or int to byte. If
the conversion is from float to int where variable x is a
float, then int y=(int) x;. Java type casting is shown in
figure A4.
Print Function
Python only uses print () to display the output (shown
in figure A5). There are two ways to concatenate a
variable to a print statement. Python uses “,” to
display variable in the print function. Whitespace is
added automatically before the value of the variable.
To concatenate a variable to a print function i.e., using
“+” character then the data type of that variable must
always be a String.
Java has a more structured syntax. To concatenate a
variable in a print statement “+” is used.
System.out.print(); prints the strings or references
and System.out.println(); is also similar to the above
but after printing it moves the cursor to the next line.
Java print function is shown in figure A6.
Comments
Comments are text or code that is written in the
source code to make it more readable. They are not
executed. Python uses the “#” character to declare it
as a comment. For multi-line comments “#” can be
used for each line or “ “ “ ” ” ” (triple quotes) can be
used as python ignore string literals which are not
assigned to a variable (shown in figure A7).
Java uses “//” (two forward slashes) character for
single-line comment, everything after the “//” is
regarded as a comment. For multi-line comment, “ /* ”
is used at the start and “ */ ” is used at the end of the
comment (shown in figure A8). Any text or code
between them is ignored.
Separators
Python uses whitespace and does not have a specific
symbol to declare a line break (shown in figure A9).
Java uses semicolon “;” character to separate two lines
from each other (shown in figure A10). After every
statement if “;” is not used, it will raise an error.
Programmers are emphasized to check the “;”, as a
massive error will arise even if a single “;” is missed.
Indentation or Curly brackets
Python uses whitespace to indicate if the code is
inside a loop or not (shown in figure A11). If the codes
are inside a loop it is indented and to indicate code
outside the loop it is outdented. The whitespace
indentation makes the code readable. If there is a
mistake in the indentation then an error will arise.
Java uses curly brackets to determine if the code is
inside a function or loop, etc., (shown in figure A12). If
the code is inside curly brackets then it means it is
within the function. It does not need to follow the
indentation rule which makes their code messy to
read.
Operators
Python has many forms of operators such as
arithmetic operator (+, *), assignment operator (=,
+=), comparison operator (= =, <), the logical operator
(and, not), identity operator (is, is not), membership
operator (in, not in), the bitwise operator (^, |)
(shown in figure A13).
Java also has different types of operators, some of
them are also similar to Python. Java has arithmetic
operation like ++ and -- for increment and decrement,
unlike Python. Java does not have an identity and
membership operator. For a logical operator in Java
&&, ||, ! are used for and, or, not respectively (shown
in figure A14).

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 07 Issue: 08 | Aug 2020 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
© 2020, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page 4392
Strings
In Python, strings can be written using a single or
double quotation (shown in figure A15). There is no
character datatype in Python. Multiline strings can
also be declared using triple quotes. In Python, strings
are array and there is negative indexing in Python.
Strings in Python are also immutable. There are many
built-in methods for the string. The format method in
string helps in combing string and number without
type-casting. An escape character ‘\’ if an illegal
character inside a string is needed.
Java string can be declared using double quotation “ ”
(shown in figure A16). Java has a separate datatype
called character datatype assigned with a single
quotation ‘’. Strings are treated as objects in Java.
Strings are immutable in Java but can be made
mutable using StringBuffer and StringBuilder. Java
also has an escape character like Python. There are
built-in methods for a string in Java. Multiline string
literals are not supported in Java.
User Input
In Python, the keyword “input” is used for the user to
input value (shown in figure A17). Everything a user
input Python recognizes it as a string data type. So,
casting becomes necessary if a specific data type value
is needed from the user.
Getting input from the user is not as simple in Java as
in Python. The Scanner class object is created and
java.util.Scanner is imported so that user can input
values. “nextInt()”, “nextFloat()”, “nextLong()”,
“nextDouble()”, “next().charAt(0)” methods are used
to get integer, float, long, double, character inputs
respectively from the user (shown in figure A18, A19).
“next ()” or “nextLine()” is used to get a string.
Conditional statements
A conditional statement allows a certain group of code
to execute according to the true or false of the given
condition. Python has if, else, elif and nested if
condition (shown in figure A20). It does not include
switch-case like other programming language and
“elif” is used instead of “else if”. As Python relies on
indentation, in order to specify that the code belongs
to the specific condition, the block of code must be
indented and after the condition, there must be a “:”
character. Ternary operators or shorthand methods
for if or if-else is present in Python which is used
when there is only one statement to be executed and it
is put in the same line.
Java’s conditional statements include if, else, else if,
switch case (shown in figure A21). Both the language,
Python and Java use the following logical conditions <,
>, <=, >=, = =, !=. The condition must be inside a “()”
bracket and the statements or code to be executed
inside a “{}” bracket. Java has shorthand if-else to
replace simple if-else condition.
Loops
Python has while loop, for loop and nested loops
(shown in figure A22). There is no do-while loop in
Python. For loop in Python doesn’t require to be
indexed beforehand, it is more of an iterator method.
Unlike other programming languages, Python for loop
can have an “else” method which is to be executed
when the for loop is over. There can be nested for
loops. While loop in Python is executed as long as the
condition is true. In Python, variable in while loop is to
be initialized before the loop and incremented inside
the loop. There can be nested while loops. Python
while loop can have else method after the completion
of the loop.
Java has for loop, while loop, nested loop and do while
loop (shown in figure A23). For loop in Java is used
when the number of iteration is fixed. There is also a
“for-each” loop only used for iteration through an
array. If the number of iteration is unfixed use “while”.
The variable needs to be initialized first and
incremented or decremented inside the loop. The do-
while loop is used if the codes need to be executed at
least once and the further repeated execution will
continue only if the condition is true.
To terminate the current loop “break” keyword is
used for both the language. Java switch also uses a
break statement to jump out of the loop. Continue in
Python and Java is used to stop the current ongoing
iteration and go on with the next. Pass statement is
only used in Python. It is a null statement. Although
the interpreter doesn’t ignore it, nothing happens
when it is being executed.
Classes and Objects
Classes are logical grouping which helps in the reuse
of data as part of a code. An object is a collection of
data and methods and class is the blueprint of that
object. The role of an object is represented by
attributes (variable) and action by the method. Python
is an object-oriented programming language and
entirely everything is an object. Python classes are
declared using the keyword “class” (shown in figure
A24). In the example, “s” is the object (instance) of the
class “Stu”. “self” refers to the current class instance. It
used to access variables that belong to the class. The
memory location of the instance that is created is
internally passed to “self”. Python also has a special
constructor method which will be discussed later.
Variables are of two types in a class i.e., class variable
(or static variable) and instance variable. The class
variable is shared by all instances of a class whereas
instance variables are variables that create a separate
copy of thevariable in every instance. Class variables

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 07 Issue: 08 | Aug 2020 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
© 2020, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page 4393
can be accessed from any method within the class. The
instance variable requires an instance method to
access it.
Java is an OOP language. In Java, everything is
correlated with class and object. The “class” keyword
is used to define a class in Java (shown in figure A25).
The object in java is used to access members of a class.
The “new” keyword is used when creating a new
object. A Java program can only have one main class
with only one main method. A constructor in Java has
the same name as the class name. Whenever an object
is created in both the language, at least a default
constructor is enforced even if the programmer does
not write a constructor. In the example shown, the
constructor is not present so it is automatically added
during compilation. The static variable (or class
variable) in Java is common for all the instances in
class and uses the “static” keyword. Instance variables
are defined outside method and without the static
keyword. The local variable is inside a method. Java
access modifiers which will be studied in the further
topic.
Function and Methods
Python function is a block of code that is executed
when called. There are built-in functions and user-
defined functions. To indicate as a function “def”
keyword is used (shown in figure A26). If there is a
function say, “def func(x):” then it can be called using
“func(a)”. Here, x is a parameter and a is an argument.
There is also a term called arbitrary argument
denoted by “*args” if the number of arguments to be
passed is not specified. Python also supports keyword
arguments and the order of the argument doesn’t
matter here. Every argument passed to a function is
treated as the same datatype. Pass statement can be
used to avoid error if the function is empty. If there is
no return statement in a function then “None” is
returned. The function or method in Python supports
multiple return values simultaneously. A function
written inside a class is called a method (shown in
figure A27). Python has a special method called
constructor i.e., def __init__ (self, parameter):. It is used
to declare and initialize an instance variable. The first
parameter for constructor and instance method is
“self”. The instance method in Python is obligated to
object and act on instance variables. Class methods act
on class variables and are bound to the class which
doesn’t require class instance creation.
“@classmethod” is used for a class method. The static
method is used when some operation is associated
with class but does not need the class or instance to
process. “@staticmethod” is used for static methods.
The team won’t dive into details on this topic.
In Java, function and method are the same. There are
many predefined methods in Java. Access modifier,
static or not, return type, and name of the method
must be present in a method while declaring it (shown
in figure A28). The return value must be of the same
data type with the return type declared when the
method is initiated. Return type “void” is used when
there is no return value. The arguments passed must
be in the same order as their respective parameter in
the method. If a method is static it can be called
without creating an object as it belongs to the class.
The static method can access a static variable and
static block only while the non-static method can
access the static variable, non-static variable, static
block, and non-static block. Java constructor is
different from the Java method. A constructor in Java
cannot have any return value (shown in figure A29). A
constructor cannot be abstract or static or final and it
can be overloaded but cannot be overridden.
Overloading in Java will be studied in further topics.
Scope
The scope is the region where a variable is accessible
and that region is where the variable is created. In
Python, a variable that is created inside a function or
method is called a local variable, and the region is
called local scope. A local variable cannot be accessed
or modified outside the function. A variable created
outside any function is known as a global variable and
it comes under the Global scope. This variable can be
accessed from any part of the program even inside a
function also. The global keyword is used if a global
variable is to be modified inside a function (shown in
figure A30).
In Java set of curly brackets define a scope (shown in
figure A31). A variable declared inside a class but
outside any function is call class variable scope. It can
be accessed and modified from anywhere inside the
class. If a variable is declared inside a method, then it
is called local or method variable scope. It can be
accessed and modified inside the specific method only.
If a variable is declared inside the block scope that is
in between curly brackets, no matter if the block of
quotes exists on its own or belong to the if, while, or
for statements then the variable will only be
accessible and modifiable inside the block scope.
There is a static and non-static block in Java. If the
static block is present then, it is executed before the
main block. A static block can access static variables
only. Non-Static block can access the static and non-
static variables.
Object-oriented programming (OOP)
Object-oriented programming is a programming
paradigm that is based on the object containing data
members and methods. It increases the flexibility and
maintainability of programs by making the data
member and methods come together. Class is a
blueprint for the object. Class and object will be

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 07 Issue: 08 | Aug 2020 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
© 2020, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page 4394
discussed later. The four main characteristics of
object-oriented programming are abstraction,
encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism.
a) Abstraction
Hiding certain details and showing only essential
information to the user is an abstraction of data.
In Python, the abstract method is declared but
doesn’t have any implementation (shown in figure
A32). A class having one or more abstract
methods is called an abstract class. Abstract class
can’t be instantiated and to implement the
abstract method sub-class is required. Python by
default doesn’t provide abstract class, so it comes
with a module named ABC (Abstract Base Classes)
and uses the keyword “@abstractmethod” as a
decorator to make a method abstract.
In Java, a class declared with the “abstract”
keyword is called abstract class (shown in figure
A33). It can have abstract and non-abstract
methods. An abstract method cannot be
instantiated (an object cannot be created) but can
have a constructor, static, and final method. A
method is abstract if it is declared with the
keyword “abstract” and doesn’t have an
implementation (i.e., no method body). The
abstract method must always be followed with a
“;”. The Abstract method can only be used with an
abstract class in Java.
b) Inheritance
Inheritance is the process of creating new classes
from existing classes so that the new class can
acquire all the features of the existing class. It
provides code reusability. In Python, the new
class created is called the child class or superclass
and the class from which it is inherited is called
parent or subclass. In Python, a base class can be
inherited by a derived class by just mentioning
the base class in the bracket (shown in figure
A34). The child constructor overrides the
inheritance of the parent constructor (i.e.,
constructor overriding) so, to keep the parent
constructor add a call of the parent’s “init”
function. The “super()” is used to call the parent
class constructor or method from the child class
(shown in figure A35). The “super()” function
helps the child class to automatically inherit all
the properties and methods of the parent class.
Python supports single inheritance, multiple
inheritances, multilevel inheritance, hierarchical
inheritance, and hybrid inheritance.
Java uses the keyword “extends” for making a
derived class from the existing class. In Java, the
new class is called the child or subclass and the
inherited class is called the parent or superclass.
The “final” keyword when used in a class prevents
it from being inherited (shown in figure A36). Java
supports single inheritance, multilevel
inheritance, hierarchical inheritance, and hybrid
inheritance. Java doesn't support multiple
inheritances to avoid the ambiguity caused by it.
In Java, constructor chaining refers to child class
constructor calling the parent class constructor.
The keyword “super” is used. When a shadowing
problem occurs i.e. when there is a name conflict
of variables within a setter between instance
variable i.e., global variable and a local variable,
the “this” keyword is used (shown in figure A37).
c) Polymorphism
Polymorphism is one of the important features of
object-oriented programming which allows a
single action to be performed in different ways. If
a class contains the same method with different
implementation then the class is polymorphic.
Polymorphism makes code easy to change,
maintain, and increase flexibility. In Python,
operator overloading where an operator performs
additional action is an example of polymorphism.
Functions such as “len()” that can be executed
with multiple data types are polymorphic. Python
allows duck typing where the object that is not
checked while invoking the method on the object
and any object is accepted if the method is found
in the object (shown in figure A38). Method
overriding where the subclass method replaces
and overrides the same method in the superclass
during inheritance is also an example of
polymorphism.
In Java, polymorphism means one entity
processing multiple forms (shown in figure A39).
All Java objects are polymorphic. Polymorphism
in Java has two types that are runtime
polymorphism (or dynamic polymorphism) and
compile-time polymorphism (or static
polymorphism). Compile-time polymorphism
includes method overloading and operator
overloading. Runtime polymorphism includes
method overriding. Java doesn't support user-
defined operator overloading. Method
overloading in Java allows us to have more than
one method with the same name but the
parameters of the method are to be different in
number or sequence order type of parameter. The
method with the same name can the same a
number of parameters are in the superclass and
subclass the method to be Court is determined at
runtime by JVM. Method overloading and
overriding will be discussed in detail later.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 07 Issue: 08 | Aug 2020 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
© 2020, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page 4395
d) Encapsulation
Encapsulation is wrapping up of data under a
single unit. It is a protective shield that prevents
unauthorized access to data from outside the
shield. Access modifiers which will be discussed
later play an important role in data encapsulation.
Python has a public, protected, and private
members (shown in figure A40). Java has public,
private, default, and protected members (shown
in figure A41). Encapsulation makes our code
cleaner and easy to read. Encapsulation is a way
to achieve data hiding in Java so that other classes
will not be able to access data in private data
members. In Java, by providing only the getter
and setter method we can make the class write-
only or read-only. If all the variables in the class
are declared private and the getter and setter
method public to set and get values of variable
then it is considered as encapsulation.
Access modifier
Like all the object-oriented programming languages,
Python also has access modifiers i.e., private, public,
protected. The access modifier helps in preventing the
data from being exploited and secure it from
unauthorized access. With the help of the underscore
“_”, Python specifies access modifier. The members
declared as public are accessible from outside the
class by everyone. The members declared as protected
are accessible from within and outside the class but
only in a class derived from i.e., a child or subclass.
Prefix single underscore “_” being added to a data
member of a class make it protected (shown in figure
A42). The private members are only accessible within
the class and the member for a class are made private
by adding double underscore “__” (shown in figure
A43). All members in a python program are by default
public.
Java has four access modifiers i.e., private, default,
protected, and public. Private data members and
methods are accessible only inside the class where
they are created and then not accessible anywhere
else. The keyword “private” is used for it (shown in
figure A45). When no access modifier is specified, then
it is called the default access modifier. Default data
members and methods are accessible only in the
package where they are created. They are not
accessible inside the different packages. The Protected
data members and methods can be accessed in the
same package and extend the class in different
package i.e., through child class. The keyword
“protected” is used for it (shown in figure A44). Public
data members can be accessed from anywhere inside
and outside the package or class. The keyword
“public” is used. This access modifier comes in handy
during data encapsulation of OOP.
Method Overloading & Overriding
Method overloading occurs when there is more than
one method with the same name but different
parameters in the class. Method overriding is a
concept of replacing the same method with the same
number of parameters in the child class that is defined
in the parent class. Both method overloading and
overriding are features of polymorphism. Method
overloading is not supported in Python (shown in
figure A46) because Python only keeps the last
declared method. Python supports method overriding
(shown in figure A47). Python constructor supports
overriding only.
In Java, method overloading happens at compile time
(shown in figure A48) and method overriding at
runtime (shown in figure A49). Method overloading
gives better performance then method overriding
since overloading is done at compile time. Static
methods can be overloaded but it cannot be
overridden. Methods like Private and final can be
overloaded but cannot be overridden. In method
overriding, the return type can be the same, or return
type may vary in the same direction as the derived
class. In method overloading, the return type can be
the same, or vary. Java constructor can only be
overloaded not overridden.
Exception handling
Exception handling is the process done by the
programmer to handle the run-time errors leading to
termination of the normal execution of a program due
to erroneous input by the user, network connection
problems, etc. There are many in-built exceptions in
Python that are raised when the Python interpreter
encounters an exception. The code or operation which
can raise an error are placed in the “try” block, the
exceptions are then handled in the “except” block. The
“finally” block is used when there are certain codes
that need to be executed regardless of the exception
being handled or not (shown in figure A50). Python
also has specific exceptions. If the exception is not
executed and else block is also present only then else
block will be executed. Python also can throw an
exception by using the “raise” keyword.
In Java, the “try” block must be accompanied by either
a “catch” or “finally” block or both “catch” and “finally”
block (shown in figure A51). The “try” block must
always come before a “catch” block. If “finally” block is
to be used, then it should be predated by a “try” block
or try-catch block. The block of code where an
exception can occur is placed in the “try” block and
“catch” block handle it. The “finally” block contains
code that is to be executed regardless of the
occurrence of the exception. The “throw” keyword is
used inside a method and can only throw a single
exception. The “throws” keyword is used to declare

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 07 Issue: 08 | Aug 2020 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
© 2020, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page 4396
multiple exceptions that can occur in the statements
present in the method. It is used along the side of the
method signature. There can be multiple catch blocks,
where the most specific catch block must be followed
by a generic catch block so that it can handle the
unexpected exceptions.
File handling
Python has an inbuilt method for reading, writing, and
creating files so importing an external package is not
needed. To open a specific file in a specific way “open
()” function along with the mode as a parameter is
used. The different modes of operations are r (read-
only) it arises an error if the file does not exists,
w(write) it creates a new file if it does not exist,
a(append to the end of the file) it create a new file if it
does not exist, x(write) create the specified file and
return an error if the file exists, t(text mode),
b(binary mode), +(open a file for updating) (shown in
figure A52). The OS module is imported and
“os.remove()” is used to delete a file (shown in figure
A53).
Java has several different methods for file
management. Java uses the I/O package to work with
different operations on a file. java.io.File is imported
and an object of the file class is created specifying the
file. Java uses the concept of the stream for input and
output in a file. To create a file “createNewFile()” is
used (shown in figure A54) and this method returns
true if the file is successfully created and false if
already exists. A try-catch block is necessary for when
the file cannot be created for some reason throwing an
ioException. The fileWriter class and “write ()”
method is used to write on a file (shown in figure
A55). The delete method is used for deleting a file. The
Scanner class is used to read a file (shown in figure
A56). The file methods such as “getName()”,
“canWrite()”, “length()”, etc., are used to get
information for a file and delete() to delete a file
(shown in figure A57).
5.2 Code Implementation
The team implemented the QuickSort algorithm and Tic-
Tac-Toe game in both Java and Python and also analyzed
the result in terms of Lines of code, file capacity, and
speed.
a) Quick Sort Algorithm
Only the code for the QuickSort algorithm was from
the GeeksforGeeks website [18] so as to achieve more
reliability in the structure of the algorithm. The team
added additional code for reading text files that
contain the numbers to be sorted and run-time
calculations. The team created four text files
containing 100000, 500000, 1000000, 1500000
randomly generated numbers respectively. The
sorting algorithm was then executed using each text
file for both the languages. For Python, the
“%%timeit” Jupyter magic function is used to calculate
the approx. execution time. For Java, “Instant.now()” is
used to calculate the elapsed time. Python consumed
more time than Java for the program to be executed in
all the four cases. Since the algorithm is for sorting,
the program in both the language executes faster
when executed a second time. So, only the first
execution is considered for this report. Java will be a
better choice for a large set of entries as it executes
faster than Python.
From Table 1, it is observed that Java is faster than
Python, and Figure 4 displays the graph for the
comparison.
Table 1: Quick Sort Execution Time Comparison
Number of
Integers to
be Sorted
JAVA
PYTHON
1,00,000
334ms
753ms
5,00,000
877ms
4480ms
10,00,000
1528ms
9140ms
15,00,000
2125ms
14200ms
Fig-4: Quick Sort Execution Time Comparison Graph
From Table 2, it is observed that Python has lesser
lines of code and file size when compared with Java.
Figure 5 and Figure 6 displays the graph for the
comparison.
0 5000 10000 15000
100000
500000
1000000
1500000
334
877
1528
2125
753
4480
9140
14200
Time in millisecond
Number of integers
Quick Sort Execution Time Comparision
python
java

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 07 Issue: 08 | Aug 2020 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
© 2020, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page 4397
Table 2: File Size and Lines of Code Comparison in
Quick Sort
Programming
Language
Lines of
Code (LOC)
File Size (in
bytes)
Python
22
1372
Java
57
1533
Fig-5: Quick Sort File Size Comparison
Fig-6: Quick Sort Lines of Code Comparison
b) Tic-Tac-Toe Game
The team implemented the game tic-tac-toe for two
players. There is an option for the number of times
that the players want to play the game i.e., a game for
one round only or three rounds or five rounds. The
players input the name they want to be represented
and randomly a player will be chosen using the
random method in both the languages i.e., Java and
Python. According to the randomly chosen player,
markers will be inserted respectively. The board of
the game has 9 positions and the game will be
continued until and unless there is a win or tie. For the
game of three or five rounds, the player name and the
chosen marker will not be changed and will be flipped
together until the game is over. The score will be
displayed for every round and the final score along
with the execution time is displayed after the game is
over completely. The execution time differs according
to the time taken by the players to input the value. The
team only considered the play where the player wins
and the input is given at a somewhat fast speed to
analyze the execution time. The program in Java is a
bit complex in structure and longer in length than the
program written in Python. However, the Java
program executes faster in all cases than Python.
From Table 3, it is also observed that Java is faster
than Python and Figure 7 displays the graph for the
comparison
Table 3: Tic-Tac-Toe Execution Time Comparison
Number of
Rounds
Python
Java
1
12.3sec
11sec
3
31.7sec
29sec
5
51.3sec
46sec
Fig-7: Tic-Tac-Toe Time Comparison
From Table 4, it is also observed that Python has
lesser lines of code and file size when compared with
Java. Figure 8 and Figure 9 displays the graph for the
comparison.
1250
1300
1350
1400
1450
1500
1550
python java
File Size in Byte
Quick Sort File Size Comparision
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
python java
Lines of code
Quick Sort Lines of Code Comparison
0 20 40 60
1
3
5
11
29
46
12.3
31.7
51.3
python
java
Time Comparision for Tic Tac Toe Game

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 07 Issue: 08 | Aug 2020 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
© 2020, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page 4398
Table 4: File Size and Lines of Code Comparison in
Tic-Tac-Toe
Programming
Language
Lines of
Code (LOC)
File Size (in
bytes)
Python
213
10729
Java
372
8583
Fig-8 Tic-Tac-toe File Size Comparison
Fig-9 Tic-Tac-Toe Lines of code Comparison
6. FUTURE SCOPE
Due to certain limitations where the major drawback was
a time restraint, the team failed to consider more than two
languages. Only some basic syntax and features are
considered in this report. There are many important
characteristics that need to be considered which were not
included in this report. So, it will be engrossing to compare
different other languages along with a deep analysis of the
language. Although Python is slow, why it is favored for
use in Big Data, Machine learning, Artificial Intelligence,
etc. can also be discussed. An experiment can be
conducted where some novices are made to undergo a
course in the language and observe their performance.
Factors such as security, reliability, durability, and
maintainability may be considered during the comparison.
Comparison of language on the basis of their uses and
which would be favored for the same applications as
which language is better to be used for web development
can be an ideal topic for further research.
7. CONCLUSIONS
The team conducted an analysis for which programming
will be better for a beginner such that they do not lose
interest and confidence in the process. The team selected
only two languages i.e., Java and Python which may not be
the best option for some cases. The team acknowledges
the fact that there are many other programming languages
which surpasses the two mentioned languages. Python
and Java were preferred for the fact that they are popular
and there is a vast community that supports them [14,15].
The vast community for these two languages plays an
important role since when a beginner encounters an
obstacle or does not understand a concept, they can seek
help from the respective communities.
The team inferred that both the languages considered in
this report have their own advantages and disadvantages
in their respective fields. It cannot be said with conviction
that one of them is better than the other. Although Java is
somewhat complex than Python in structure, it provides a
better understanding of memory management and is more
secure. Python is short, simple, and easy. A novice can
easily understand a Python program for it is written in
simple English. In Python since indentation is compulsory,
it makes the code more readable. However, this is not the
case for Java as there is no effect for indentation and the
whole program can be written in one line to make it look
short. The use of semicolon which indicates the end of the
line in Java is sometimes overlooked which leads to a
major compilation error. Python being dynamically typed
leads to longer execution time as the variable type is
checked during run time whereas Java is statically typed
so the exact datatype for variables is known during
compilation leading to faster execution than Python.
Most of the programming language has similar
fundamentals, therefore regardless of which language is
chosen the person can learn another programming
language easily. The novice must not keep changing the
language before mastering it as it will lead to a loss of
confidence. So, the novice should choose the programming
language according to the goals they prefer. If the person
would like to go for app development, then choose Java or
Swift or Flutter. If the person wants to create a game than
a language like JavaScript, Java, C or C++ may be preferred.
If the person is interested in web development or Artificial
Intelligence, etc., then language like Python, JavaScript,
0
2000
4000
6000
8000
10000
12000
python java
File Size in Byte
Tictactoe file size comparision
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
python java
Lines of code
TicTaeToe Lines of code Comparison

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 07 Issue: 08 | Aug 2020 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
© 2020, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page 4399
Ruby will be favorable. Thus, a beginner must first know
what he/she would like to work on in the future or pick an
area of interest. After that, according to their interests, the
language must be chosen.
8. REFERENCES
[1] Monica, N., O. Ogbuokiri Blessing, and O. Okwume
Benedette. "Comparison of python and java for use in
instruction in first course in computer programming."
[2] Insanudin, E. "Implementation of python source code
comparison results with Java using bubble sort
method." Journal of Physics: Conference Series. Vol.
1280. No. 3. IOP Publishing, 2019.
doi:10.1088/1742-6596/1280/3/032027
[3] Bogdanchikov, A., M. Zhaparov, and R. Suliyev.
"Python to learn programming." Journal of Physics:
Conference Series. Vol. 423. No. 1. IOP Publishing,
2013.
doi:10.1088/1742-6596/423/1/012027
[4] Kasurinen, Jussi. "Python as a programming language
for the introductory programming courses." (2007).
[5] Åkesson, Tobias, and Rasmus Horntvedt. "Java, Python
and Javascript, a comparison." (2019).
[6] Pellet, Jean-Philippe, Amaury Dame, and Gabriel
Parriaux. "How beginner-friendly is a programming
language? A short analysis based on Java and Python
examples." (2019).
[7] Adawadkar, Kalyani. "Python Programming-
Applications and Future." International Journal of
Advanced Engineering and Research Development.
http://ijaerd. com/papers/special_papers/IT032.
pdf (2017).
[8] Fatima, N., and S. Arabia. "Performance comparison of
most common high level programming
languages." International Journal of Computing
Academic Research (IJCAR) 5.5 (2016): 246-258.
[9] Srinath, K. R. "Python–The Fastest Growing
Programming Language." International Research
Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) 4.12
(2017): 354-357.
[10] Pears, Arnold, Stephen Seidman, Lauri Malmi, Linda
Mannila, Elizabeth Adams, Jens Bennedsen, Marie
Devlin, and James Paterson. "A survey of literature on
the teaching of introductory programming."
In Working group reports on ITiCSE on Innovation
and technology in computer science education, pp.
204-223. 2007.
[11] Foster, Elvis. “A comparative analysis of the C++, Java,
and Python Languages.” (2014)
[12] McMaster, Kirby, et al. "Java vs. Python coverage of
introductory programming concepts: a textbook
analysis." Information Systems Education Journal 15.3
(2017): 4.
[13] https://www.jetbrains.com/lp/devecosystem-2020/
[14] http://pypl.github.io/PYPL.html
[15] https://octoverse.github.com/
[16] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Python_(programming
_language)
[17] Donaldson, Toby. "Python as a first programming
language for everyone." Western Canadian Conference
on Computing Education. Vol. 232. 2003.
[18] Dr. R. Nageswara Rao. “Core Python Programming”.
New Delhi: Dreamtech Press; 2018
9. Appendix
A. Syntax
Fig A1. Python Variable
Fig A2. Java Variable
Fig A3. Python Casting
Fig A4. Java Casting

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 07 Issue: 08 | Aug 2020 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
© 2020, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page 4400
Fig A5. Python Print
Fig A6. Java Print
Fig A7. Python Comment
Fig A8. Java Comment
Fig A9. Python separator
Fig A10. Java separator
Fig A11. Python indentation
Fig A12. Java curly bracket
Fig A13. Python operator
Fig A14. Java operator

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 07 Issue: 08 | Aug 2020 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
© 2020, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page 4401
Fig A15. Python string
Fig A16. Java string
Fig A17. Python User input
Fig A18. Java User input
Fig A19. Java User input (output)
Fig A20. Python Conditional
Fig A21. Java Conditional
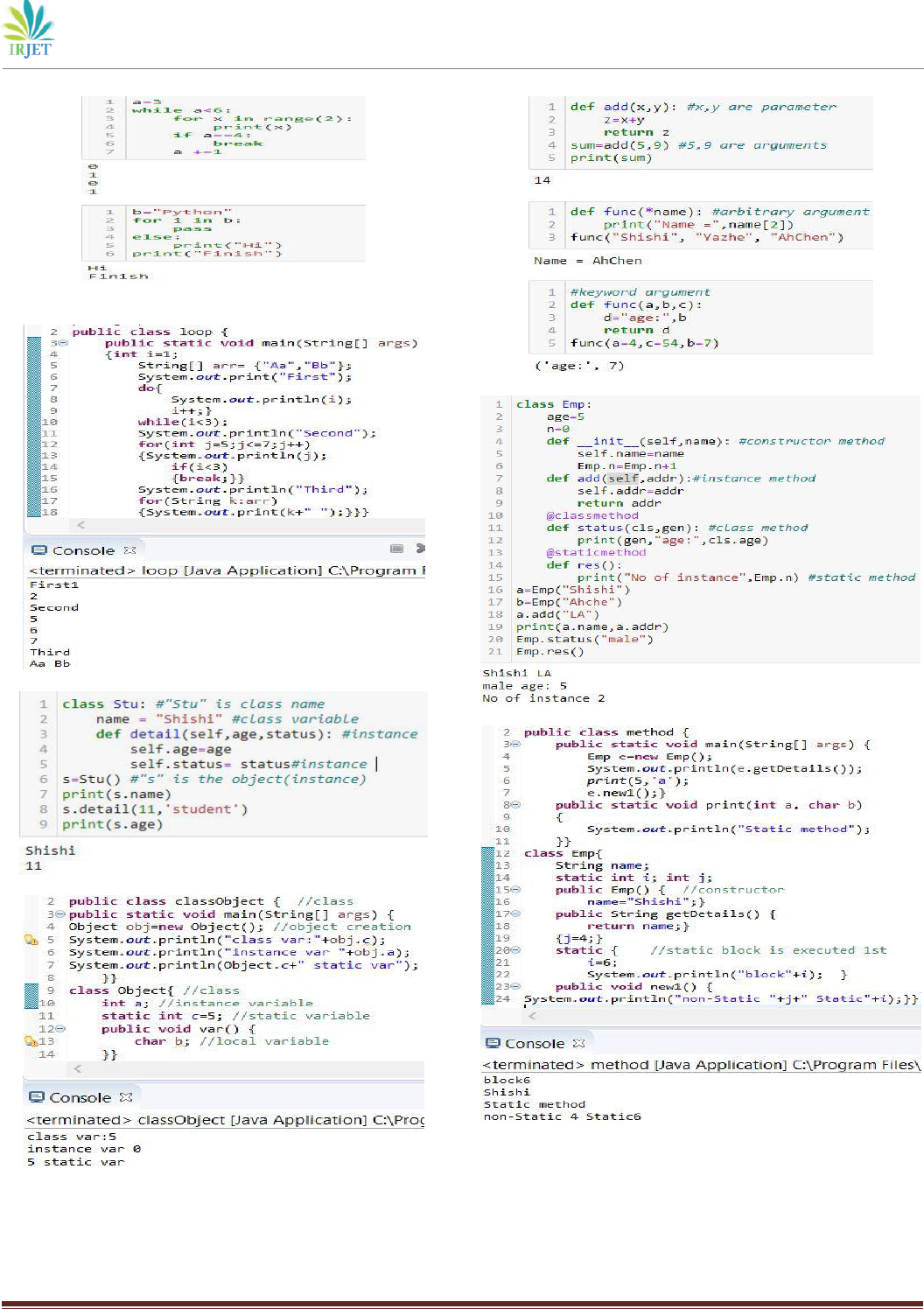
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 07 Issue: 08 | Aug 2020 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
© 2020, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page 4402
Fig A22. Python Loop
Fig A23. Java Loop
Fig A24. Python class
Fig A25. Java class
Fig A26. Python Function
Fig A27. Python Method
Fig A28. Java Method

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 07 Issue: 08 | Aug 2020 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
© 2020, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page 4403
Fig A29. Java Constructor Overload
Fig A30. Python Scope
Fig A31. Java Scope
Fig A32. Python Abstract
Fig A33. Java Abstract
Fig A34. Python Single Inheritance
Fig A35. Python super()

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 07 Issue: 08 | Aug 2020 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
© 2020, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page 4404
Fig A36. Java Inheritance
Fig A37. Java Constructor chaining
Fig A38. Python polymorphism
Fig A39. Java Polymorphism
Fig A40. Python Encapsulation
Fig A41. Java Encapsulation
Fig A42. Python protected

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 07 Issue: 08 | Aug 2020 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
© 2020, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page 4405
Fig A43. Python private
Fig A44. Java protected
Fig A45. Java Public Default Private
Fig A46. Python Overloading
Fig A47. Python Overriding
Fig A48. Java Overloading
Fig A49. Java Overriding
Fig A50. Python Exception

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 07 Issue: 08 | Aug 2020 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
© 2020, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page 4406
Fig A51. Java Exception
Fig A52. Python File handling1
Fig A53. Python file handling2
Fig A54. Java create file
Fig A55. Java Write on the file
Fig A56. Java read file

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 07 Issue: 08 | Aug 2020 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
© 2020, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page 4407
Fig A57. Java delete file
